Work Energy Theorem
Work Energy Theorem: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Work Energy Theorem
Important Questions on Work Energy Theorem
A satellite of mass , initially at rest on the earth, is launched into a circular orbit at a height equal to the radius of the earth. The minimum energy required is
of work is done in sliding a block slowly up an inclined plane of height . Taking . Work done against friction is:
A deep well is having water upto . An engine evacuates it in one hour. The power of the engine, if the diameter of the well is is
The turbine pits at the Niagara falls are deep. The average horse power developed is . The efficiency being . How much water passes through the turbine per minute. ( , )
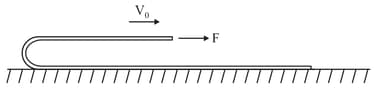
A large rope having linear mass density is being pulled by a horizontal force so that lower portion of rope is at rest and upper portion is moving with constant velocity as shown in figure. The value of is
Statement I: A truck and a car moving with equal kinetic energy are stopped by equal retarding force. Both cover an equal distance before stopping.
Statement II: A car moving towards the East suddenly changes its direction towards the North at the same speed. Its acceleration is zero.
From the terrace of a building of height , you dropped a ball of mass . It reached the ground with speed . Is the relation applicable exactly? If not, how can you account for the difference? Will the ball bounce to the same height from where it was dropped?
Given below are two statements:
Statement I : A truck and a car moving with same kinetic energy are brought to rest by applying breaks which provide equal retarding forces. Both come to rest in equal distance.
Statement II : A car moving towards east takes a turn and moves towards north, the speed remains unchanged. The acceleration of the car is zero.
In the light of given statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below
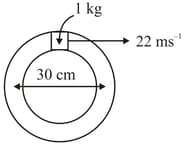
A closed circular tube of average radius , whose inner walls are rough, is kept in vertical plane. A block of mass just fit inside the tube. The speed of block is , when it is introduced at the top of tube. After completing five oscillations, the block stops at the bottom region of tube. The work done by the tube on the block is ________ . (Given ).
Body accelerates from rest to , energy is . If it accelerates from rest to , then energy is . Find
A uniform chain of length and mass m overhangs a smooth table with rd part hanging. If the chain is released from rest from this position, then its velocity as it completely slips off the table, is
If motor is pumping water with a rate of per hour from a depth of. Find power of the motor in horsepower.
A ball is thrown up with of . Calculate the work done by its weight in one second.
A well is in the form of a cylinder of radius . Water surface in it is at depth of and depth of water column is . Work done in draining out half of water from it is, ()
If force is always perpendicular to motion
Calculate the work done in joules in increasing the extension of a spring of stiffness from to is
A man was initially at rest. Then he starts walking on a rough horizontal surface. The kinetic energy increase is due to the work done by
A tennis ball thrown vertically up at rises to a maximum height of . What was the work done by resistive forces?
A stone of mass falling from height of hits the ground with a speed of . The work done by the gravitational force is
An object A moving horizontally with the kinetic energy of experiences a constant horizontal opposing force of while moving from a place X to another place Y, where XY is . What is the energy of A at Y?
